Berkelium
97
Bk
Skupina
n/a
Perioda
7
Blok
f
Protony
Elektrony
Neutrony
97
97
150
Hlavní vlastnosti
Atomové číslo
97
Atomová hmotnost
[247]
Hmotnostní číslo
247
Kategorie
Aktinoidy
Barva
n/a
Radioaktivní
Ano
Pojmenován po Berkeley v Kalifornii, městě jeho objevu
Krystalografická soustava
Hexagonální
Historie
Berkelium was discovered by Glenn T. Seaborg, Albert Ghiorso and Stanley G. Thompson in 1949 at the University of California, Berkeley.
It was produced by the bombardment of americium with alpha particles.
Berkelium was isolated in greater quantities for the first time by Burris Cunningham and Stanley Thompson in 1958.
It was produced by the bombardment of americium with alpha particles.
Berkelium was isolated in greater quantities for the first time by Burris Cunningham and Stanley Thompson in 1958.
Elektronů v obalu
2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2
Elektronová konfigurace
[Rn] 5f9 7s2
Just over one gram of berkelium has been produced in the United States since 1967
Fyzické vlastnosti
Skupenství
Pevná
Hustota
14,78 g/cm3
Teplota tání
1259,15 K | 986 °C | 1806,8 °F
Teplota varu
3173,15 K | 2900 °C | 5252 °F
Skupenské teplo tání
n/a kJ/mol
Skupenské teplo varu
n/a kJ/mol
Měrná tepelná kapacita
- J/g·K
Hojnost v zemské kůře
n/a
Hojnost ve vesmíru
n/a
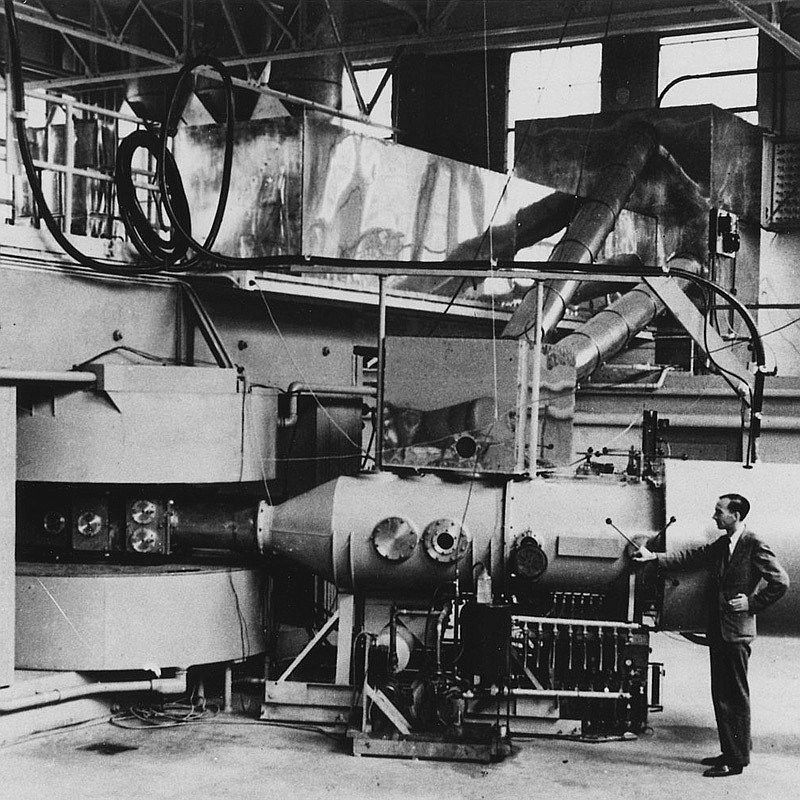
Autorská práva obrázku: Wikimedia Commons (Department of Energy - Office of Public Affairs)
60-palcový cyklotron v Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley
Číslo CAS
7440-40-6
PubChem CID číslo
23971
Atomové vlastnosti
Atomový poloměr
170 pm
Kovalentní poloměr
-
Elektronegativita
1,3 (Paulingova stupnice)
Ionizační potenciál
6,1979 eV
Molární objem
16,7 cm3/mol
Tepelná vodivost
0,1 W/cm·K
Oxidační čísla
3, 4
Aplikace
Berkelium is mainly used for scientific research purposes.
Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranic elements and transactinides, such as lawrencium, rutherfordium and bohrium.
It is also useful as a source of the isotope californium-249.
Berkelium-249 is a common target nuclide to prepare still heavier transuranic elements and transactinides, such as lawrencium, rutherfordium and bohrium.
It is also useful as a source of the isotope californium-249.
Berkelium je škodlivé díky své radioaktivitě
Izotopy
Stabilní izotopy
-Nestabilní izotopy
233Bk, 235Bk, 236Bk, 237Bk, 238Bk, 239Bk, 240Bk, 241Bk, 242Bk, 243Bk, 244Bk, 245Bk, 246Bk, 247Bk, 248Bk, 249Bk, 250Bk, 251Bk, 252Bk, 253Bk, 254Bk